Master Running Code Blues!
Most Important Factors
- Team Leadership
- Hemodynamic Directed Resuscitation
- High Quality CPR
- Early Defibrillation
- Medications
- Novel Therapies
- Post Arrest Care

1. Team leadership
- Deficits in leadership can cost lives
- ex: poor performance of CPR, decreased ROSC, decreased survival
- Benefits:
- Good leadership –> establish ROSC faster
- Proper planning (ex: role assignment) –> reduced hands-off time, less interruption, faster treatment completion
- Improved communication –> accuracy of team leader communications linked to errors
- Rolesof the team leader:
- ensures delivery of adequate compressions
- minimize interruptions
- avoid excessive ventilation
- What can you do? Take charge!
- direct all components of resuscitation
- assign tasks
- communicate clearly
- be decisive
2. Hemodynamic directed resuscitation
- Survival dependent upon restoring myocardial blood flow
- Keep coronary blood flow (CPP) >20mmHg, three ways to check
- DBP – RAP(or CVP), caveat: need A-line and central line
- DBP>25mmHg, just need A-line
- ETCO2>20
- May use these parameters to optimize CPR, guide vasopressor use, and detect ROSC
- Keep coronary blood flow (CPP) >20mmHg, three ways to check
3. High quality CPR
- Rate: 100-120/min
- Depth: 5-6 cm(2-2.4 inches)
- Allow full chest recoil
- Avoid leaning
- Chest compression fraction > 60% (minimize interruptions)
- Eliminate pulse checks
4. Early defibrillation
- Hands off for shock, charge while compressions are occurring
- Limit perishock pause to <10s
5. Medication
- Vasopressors
- Increase aortic pressure
- Improve CPP
- Improve cerebral perfusion pressure
- No definitive evidence that any vasopressor agent improves long-term survival
- Epinephrine
- Decreases microcirculatory cerebral flow
- Increased myocardial O2 consumption
- Increased post-defib ventricular arrhythmias
- Increased post-ROSC myocardial dysfunction
- Standard dose (1mg q3-5mins) MAY be reasonable
- Vasopressin – not recommended
6. Novel therapies
- ECPR not universally accepted
- best outcomes: witnessed arrest, bystander CPR w/in mins, shockable rhythm, short EMS transport time, short time to ECMO, emergent hypothermia, and PCI
7. Post arrest goals
- Optimize oxygenation and ventilation
- Decrease FiO2 for O2sat>94%
- Goal: PCO2 35-45; ETCO2 30-40
- Optimize hemodynamics
- Targeted temp management
- Comatose adult patients with ROSC after cardiac arrest (32-36C for 24 hours)
- No benefit of endovascular over surface cooling
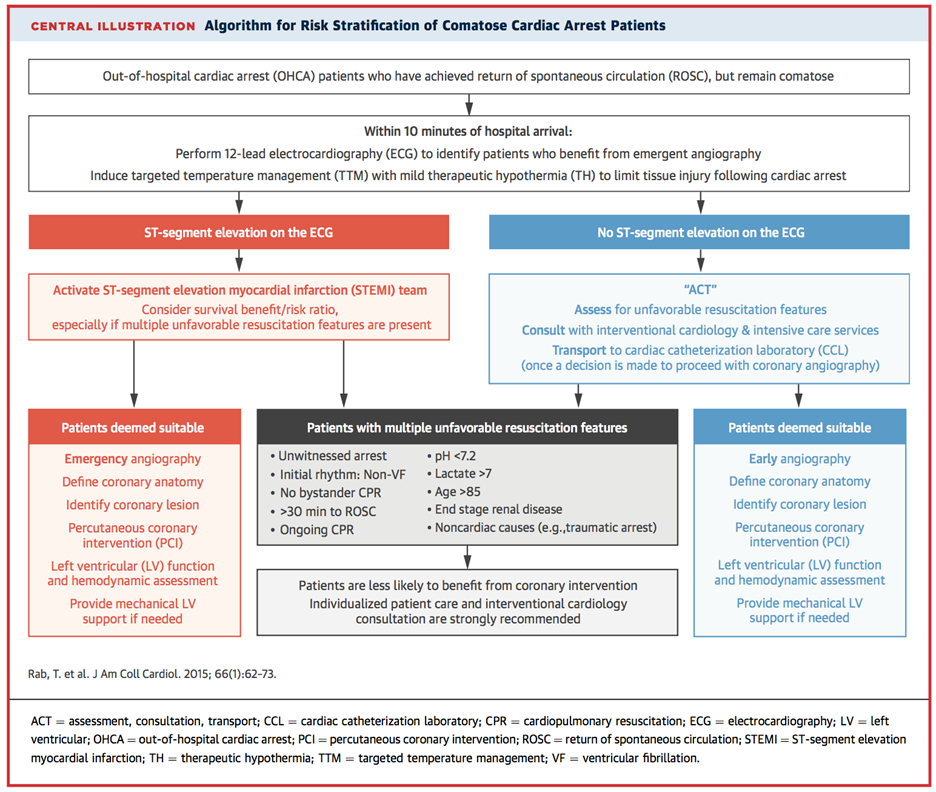
- Emergent PCI
- STEMI, NSTEMI with hemodynamic instability or refractory VF/Vfib or ongoing ischemia
Algorithm for Risk stratification of Comatose
Cardiac Arrest Patients