Mastering Vasopressor Management
Rules of Critical Care
1. Defend the blood pressure
- “True” hypotension is an emergency
- MAP<65 needs attention IMMEDIATELY
- Hypotension →Decreased DBP → Decreased coronary blood flow → Cardiac ischemia → Decreased CO → Hypotension (repeat)
- Short durations hurt brain, kidneys, heart
- Longer durations of hypotension = worse outcomes
- Push dose, immediate fluids, etc.
- FIX IT!
- MAP<65 needs attention IMMEDIATELY
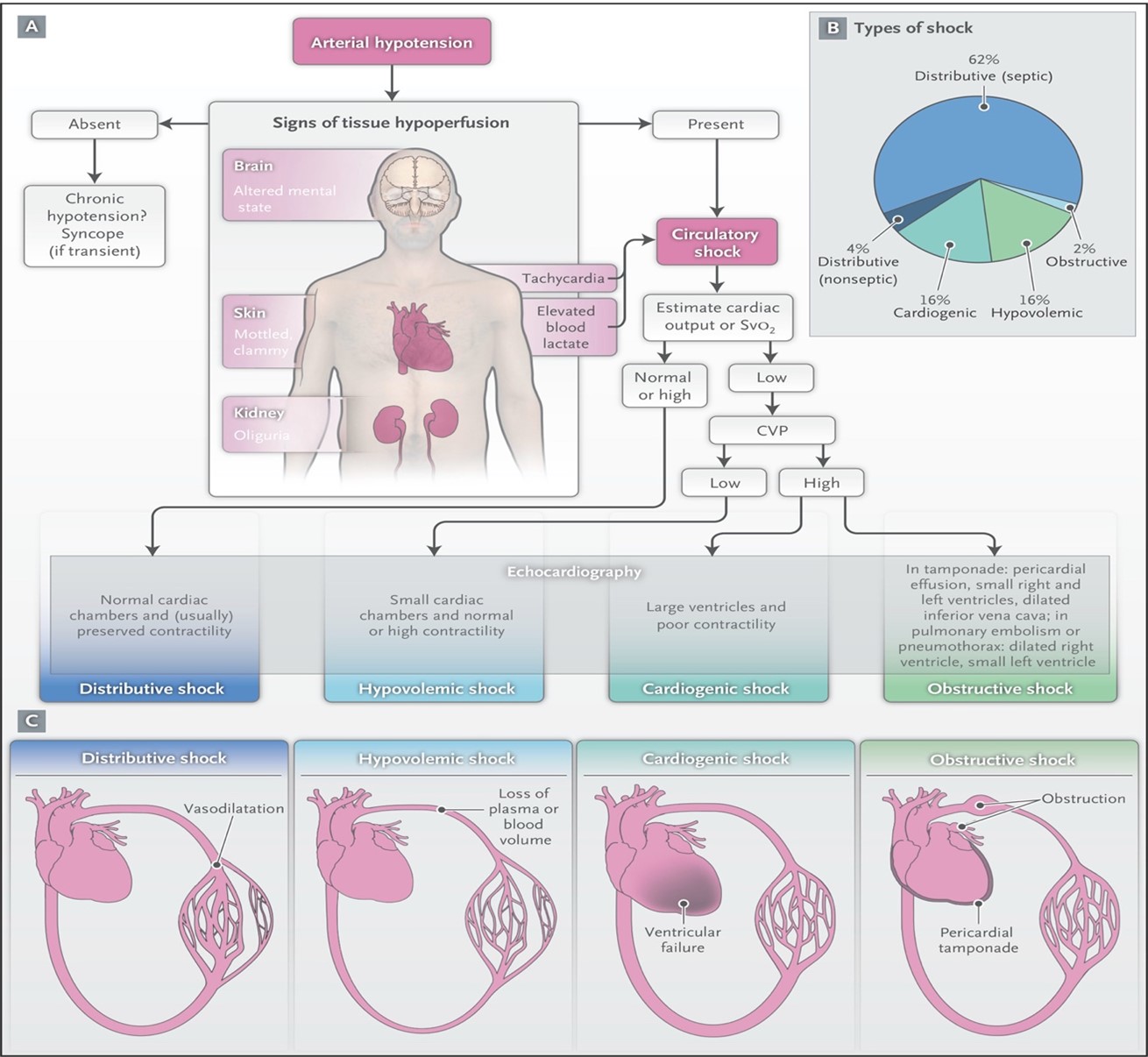
2. You MUST diagnose shock
- Always identify which type of shock!
- Stabilize/Defend BP
- Assessment of CO → Diagnose shock type
- Volume trial → Look for CO improvement
The choice of vasopressors is not always clear
- The case for Vasopressin>NE: VASST trials
- Are both studies underpowered? Is steroids+Vaso the magic solution for the truly sick?
- No consensus solution
- The comparison of NE to Dopa(SOAP II group)
- Poorly dosed Dopa in the comparison group (not studying the physiological rationale)
- NE maybe better for you (for cardiogenic shock)
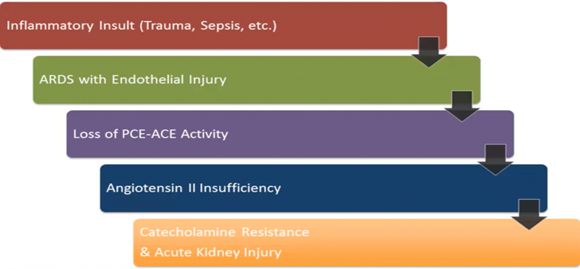
- Hypotension is due to a lack of catecholamines (just as HTN is due to an overabundance of them)
- Are both studies underpowered? Is steroids+Vaso the magic solution for the truly sick?
Alternative vasopressors: What is in the pipeline?
- Selepressin
- Vasopressin targets V1a, V1b for vasoconstriction
- Also targets Oxytocin and V2→ fluid overload and microvascular thrombosis
- Selepressin is a selective V1a agonist → targeted vasoconstriction
- Improves free water clearance (lacks V2 targeting) → less lung injury/less lung edema
- Less vascular leak(typical with Vasopressin)
- Vasopressin targets V1a, V1b for vasoconstriction
- Angiotensin II (Ang II)
- First trial: 1961, then disappeared
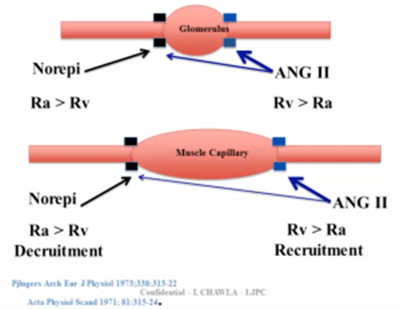
- Example: Distributive shock, s/p resuscitation, has INCREASED blood flow to kidneys → intraglomerular hypotension and AKI
- Treatment with Ang II leads to improvements
- NE leads to AFFERENT vasoconstriction
- Ang II→ EFFERENT vasoconstriction (recruits capillary beds)
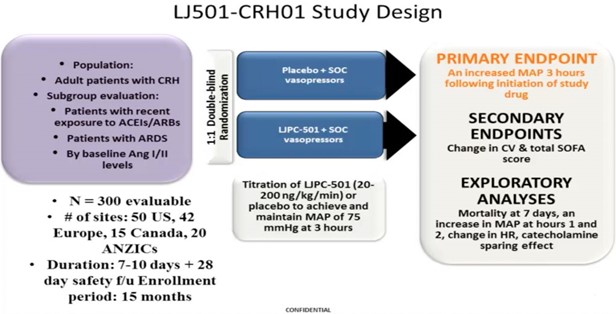
- ATHOS trial
- Low doses of Ang II can causecatecholamine sparing
- 2 outliers had HYPERtension (due to ARDS?)
- Low doses of Ang II can causecatecholamine sparing
- SEVERE ARDS causes Ang II deficiency
- Pulmonary capillary endothelium damage can restrict conversion of Ang I to Ang II
- Ang II Pilot data conclusions
- IV Ang II has a role as a rescue vasopressor
- IV Ang II may bemore useful in ARDS patients
- Currently undergoing a Phase III registration trial for Ang II as a vasopressor
- First FDA trial for a drug AS a vasopressor
- Treatment with Ang II leads to improvements