Mastering Mechanical Ventilation Basics
- Respiratory failure
- Goals
- Ventilator Definitions
- Waveforms
- Ventilator adjustments
- Troubleshooting
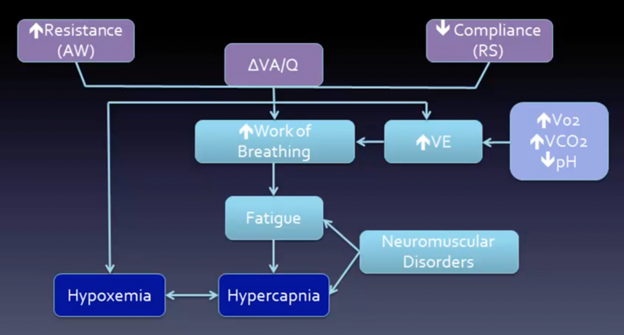
Respiratory failure:
- Type 1: hypoxic
- #1 cause V/Q mismatch
- Decreased ventilation (airway, ILD)
- Increased perfusion to normally ventilated lung (PE)
- Shunt
- ARDS, PNA, edema
- #1 cause V/Q mismatch
- Type 2: hypercarbic
- Need to correct decreased alveolar hypoventilation
- Increase minute ventilation +/- decrease dead space (if hypoxic, will correct with oxygenation)
- Need to correct decreased alveolar hypoventilation
- Treatment:
- Reverse cause + positive pressure
- Decrease work of breathing
- Restore adequate gas exchange
- Noninvasive (NIV)
- CPAP, BiPAP, cuirass
- Invasive (ETT or tracheostomy)
- volume, pressure, hybrid, or “novel” modes (i.e., APRV, NAVA)
- Reverse cause + positive pressure
Goals:
- Ventilation
- Acceptable pCO2 + pH
- Goal Pplat <30
- Decrease auto-PEEP(breath stacking)
- Oxygenation
- Goal SpO2 >88% on FiO2 <60%
- Optimal delivery of O2: (DO2) = CO x (1.34 × Hb × SaO2) + (0.003 × PaO2)
- ARDS
- tidal volume ≤ 6 cc/kg IBW (based on height)
- Conservative fluids
- Avoid VILI
Ventilator Definitions:
- Control
- Howa breath is delivered (V vs. P vs. dual)
- Triggering
- Wheninspiration starts (flow or pressure)
- Cycling
- Whatdetermines switch from insp to exp
- Time or flow sensed
- Breaths
- Mandatory, assisted, spontaneous
- Flow pattern
- Often set by the method of control
- Sinusoidal, accelerating, constant (square), decelerating
- Mode or breath pattern:
- Spontaneous, assist control (AC), intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV)
- Pressure supported (PS) or volume supported (VS)
- Scalar
- Waveforms that plot pressure, flow, or volume vs timeon the ventilator screen
- Loops
- Pressure or flow vs. volume(look like PFTs upside down)
Waveforms:
- Allows provider to:
- Assess real time changes in patient condition
- Optimize vent settings and treatment
- Determine effectiveness of vent
- Detect adverse events
- Decrease risk of mechanical complications
- Pressure waveforms
- Diagnose: air trapping, obstruction, dyssynchrony, pressures (i.e., plateau or end inspiratory hold), triggering, bronchodilator response
- Area under the pressure curve = Alveolar distending pressure
- Flow waveforms
- Detect air trapping, obstruction, bronchodilator response, triggering, dyssynchrony
- Square
- Pressure rises (higher peak inspiratory pressure)
- Decelerating
- Pressure constant
- Plateau pressure is greaterfor Square vs. Decelerating with same volume
- Volume waveform
- Can detect air trapping, leak, tidal volume, dyssynchrony
Ventilator adjustments:
- I (inspiratory) time
- Set for PRVC and PC, VC on some vents (otherwise set flow)
- PS: cycles once falls below set % of peak flow (decelerating flow)
- Decrease Ti: less autoPEEP, decrease CV effects
- Increase Ti:improves oxygenation
- Set for PRVC and PC, VC on some vents (otherwise set flow)
- Trigger sensitivity
- Increased sensitivity can lead to autotrigger/false triggering (water in circuit, heartbeat)
- Rise time
- Rate of rise of pressure (PC) or flow (VC)
- Short: may be uncomfortable, but can lead to decreased inspiratory workload
- Reduced VILI (biotrauma)
- Long: decreased Tv in pressure mode (less time at set pressure) or increased pressure in volume mode (to reach target volume)
- Short: may be uncomfortable, but can lead to decreased inspiratory workload
- Rate of rise of pressure (PC) or flow (VC)
Troubleshooting:
- Dx increased peak without change in Pplat
- Increased resistance→ obstruction, bronchospasm, biting, foreign body
- Dx increased peak and Pplat
- Decreased lung compliance(or increased Vt)
- PTX, abdominal HTN, ARDS, edema
- How to detect AutoPEEP
- Flownot returning to 0 before next breath
- Area under inspiratory curvenot equal to area under expiratory curve
- Dyssynchrony(double triggering)
- Treating airway obstruction:
- Bronchodilators
- Suction
- Prolong expiration
- Decrease I time
- Increase flow
- Sedate if necessary
- Increase extrinsic PEEP (2/3 intrinsic)
- Decreased lung compliance(or increased Vt)